Code Examples
I'm going to leave here code snippets that you can simply copy-paste in your own code to test and use for your own tools.
🟠 1. Get Selected Elements
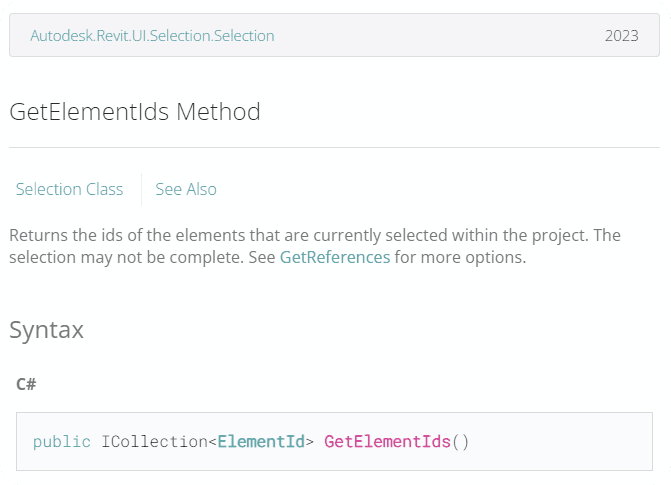
selected_element_ids = uidoc.Selection.GetElementIds()
selected_elements = [doc.GetElement(e_id) for e_id in selected_element_ids]
print(selected_elements)
filtered_elements = [el for el in selected_elements if type(el) == Wall]
print(filtered_elements)
🟠 2. Pick Elements by Rectangle
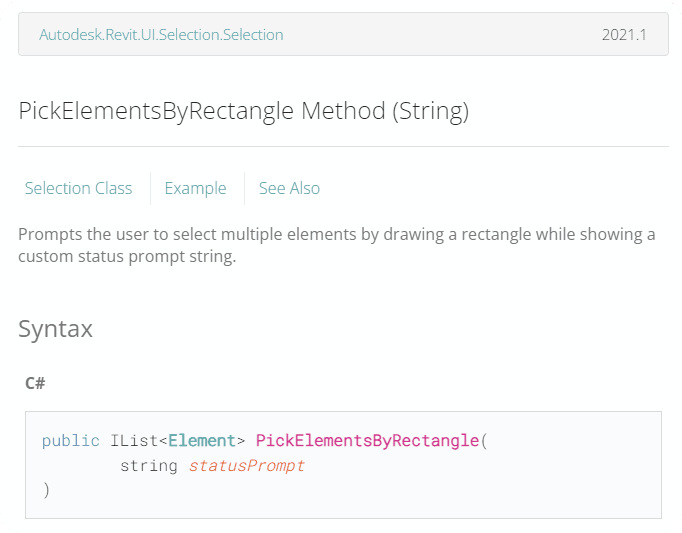
selected_elements = uidoc.Selection.PickElementsByRectangle('Select some Elements.')
print(selected_elements)
🟠 3. Pick Object
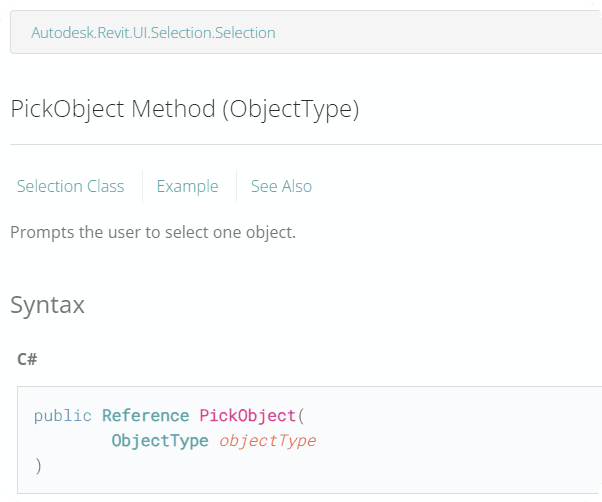
from Autodesk.Revit.UI.Selection import ObjectType
ref_picked_object = uidoc.Selection.PickObject(ObjectType.Element)
picked_object = doc.GetElement(ref_picked_object)
print(picked_object)
🟠 4. Pick Objects (Multiple)
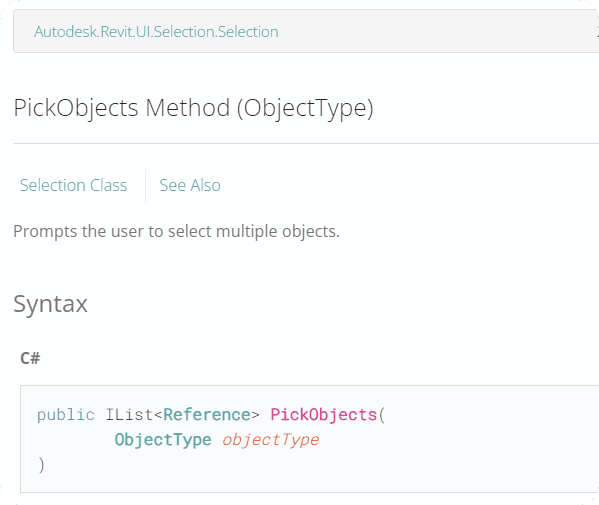
from Autodesk.Revit.UI.Selection import ObjectType
ref_picked_objects = uidoc.Selection.PickObjects(ObjectType.Element)
picked_objects = [doc.GetElement(ref) for ref in ref_picked_objects]
for el in picked_objects:
print(el)
🟠 5. Pick Point
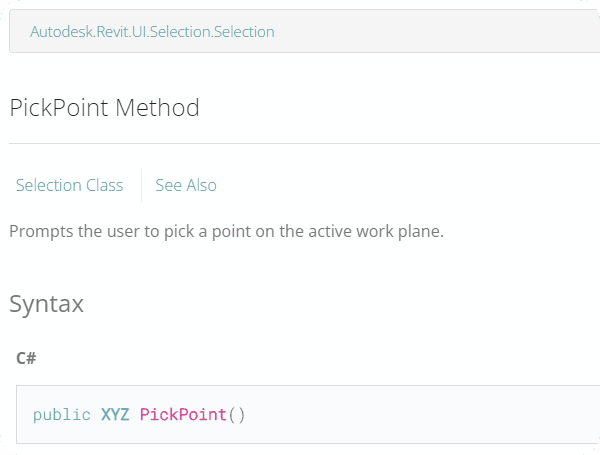
selected_pt = uidoc.Selection.PickPoint()
print(selected_pt)
🟠 6. PickBox
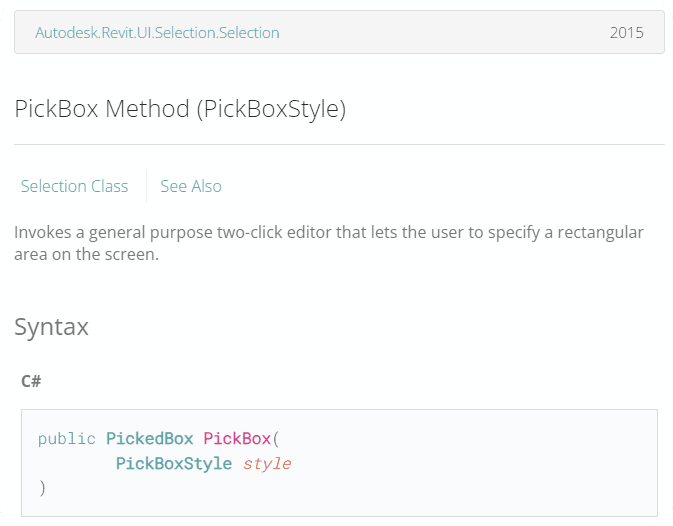
from Autodesk.Revit.UI.Selection import PickBoxStyle
picked_box = uidoc.Selection.PickBox(PickBoxStyle.Directional)
print(picked_box)
print(picked_box.Min)
print(picked_box.Max)
🟠 7. Set Selection in Revit UI
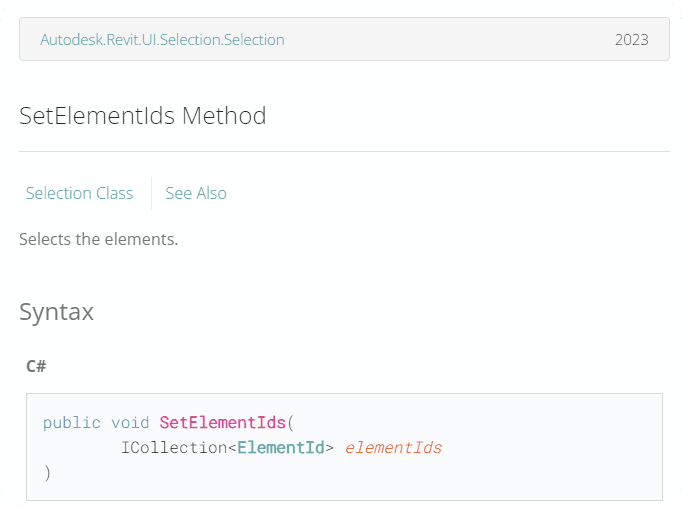
from Autodesk.Revit.DB import FilteredElementCollector
uidoc = __revit__.ActiveUIDocument
doc = __revit__.ActiveUIDocument.Document
new_selection = FilteredElementCollector(doc).OfClass(Wall).ToElementIds()
selection.SetElementIds(new_selection)
Also keep in mind that to use SetElementIds you need to use IList from .NET.
For that you would need to reference System namespace and import IList. Then you can either convert your existing python list by providing it as an argument, or add elements one by one.
💡Make sure you add elements with the same Type as you declared for the List[Type]
list_element_ids =
import clr
clr.AddReference('System')
from System.Collections.Generic import List
List_el_ids = List[ElementId](list_element_ids)
🟠 8. ISelectionFilter Example
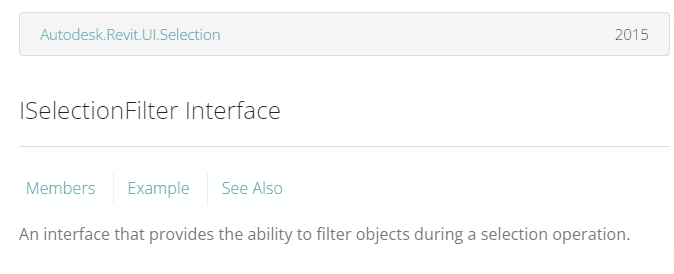

from Autodesk.Revit.UI.Selection import ISelectionFilter, Selection, ObjectType
uidoc = __revit__.ActiveUIDocument
class ISF_wall_filter(ISelectionFilter):
def AllowElement(self, element):
if type(element) == Wall:
return True
custom_filter = ISF_wall_filter()
selected_elements = uidoc.Selection.PickElementsByRectangle(custom_filter, "Select Walls")
print(selected_elements)
Want More?
I hope it was really helpful to understand Revit API Selection.
If you want to learn more and get more examples, check under Selection group in the sidebar menu.











